Humidity Emerges as Primary Threat to Texas Cold Storage Operations
Summary
Full Article
In Texas cold storage facilities where temperature typically dominates operational concerns, moisture has emerged as the primary threat to safety, efficiency, and profitability. According to Clayton Settle, Project Manager at Eldridge, humidity represents a silent saboteur that undermines cold storage operations despite often being overlooked in facility design and management.
Cold storage environments operating between 0°F and 40°F don't create humidity but rather amplify existing moisture problems. When warm, moist air infiltrates these controlled environments, three critical issues emerge: frost accumulation on cooling coils that insulates equipment and reduces efficiency, icing and fogging hazards that create dangerous working conditions, and energy waste from frequent defrost cycles and latent heat removal. The dew point, rather than simple temperature readings, determines success in cold storage design according to industry experts.
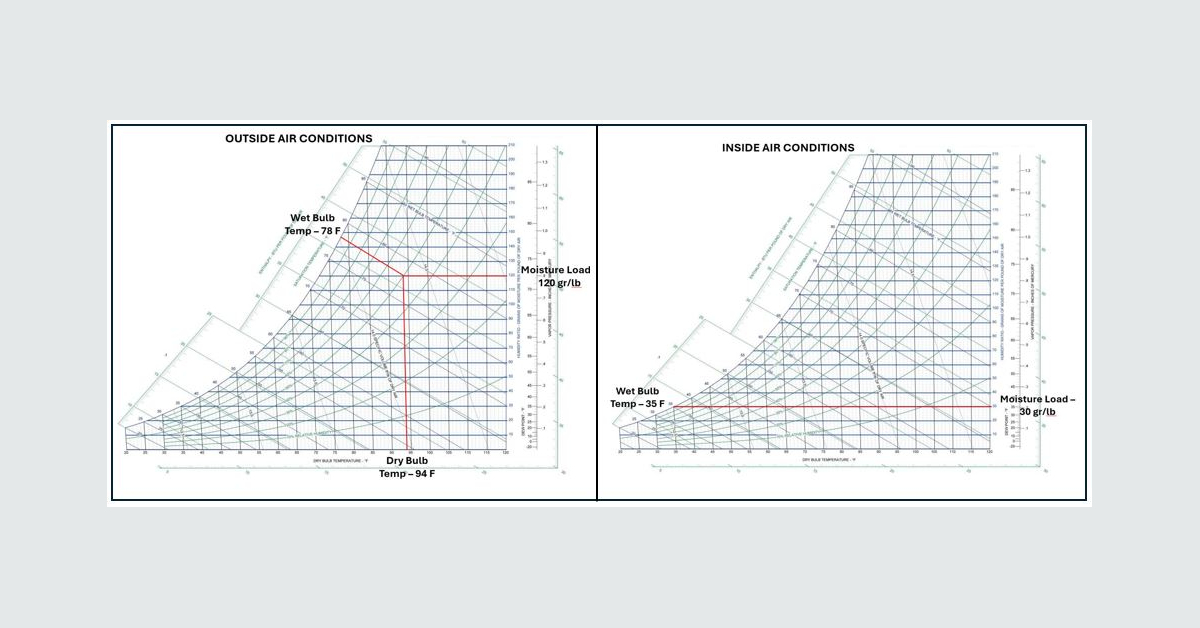
Eldridge engineers are employing psychrometric charts to model and control air's thermodynamic properties, fundamentally changing how industrial facilities approach humidity management. By plotting dry-bulb, wet-bulb, and dew point temperatures, engineers can visualize precisely when and where condensation or frost will form, enabling them to design ventilation and dehumidification systems that maintain air safely below its dew point. This approach transforms humidity control from reactive problem-solving to proactive engineering.
In a recent application, Eldridge modeled outside air conditions of 94°F dry-bulb and 78°F wet-bulb against a 35°F cold storage environment. The resulting 90-grains-per-pound moisture differential guided precise sizing of desiccant dehumidifiers, effectively preventing frost formation while ensuring both safety and energy efficiency. This methodology allows facility managers to identify high-risk zones, reduce maintenance cycles, and protect workers before hazards materialize.
The psychrometric chart has evolved from classroom diagram to practical blueprint for modern cold-chain management. By understanding air behavior in advance through tools available at https://www.eldridgeusa.com/industrial-ventilation, companies can transition from reacting to humidity problems to preventing them entirely through smarter engineering approaches that prioritize comprehensive air management over simple temperature control.
This shift in approach has significant implications for Texas businesses operating cold storage facilities, particularly in the state's challenging climate conditions. The proactive management of humidity rather than reactive temperature control represents a fundamental change in how industrial refrigeration systems are designed and maintained. For Texas companies involved in food processing, pharmaceutical storage, and logistics, this methodology could lead to substantial energy savings, reduced equipment maintenance costs, and improved worker safety conditions.
The economic impact extends beyond individual facilities to the broader Texas supply chain, where reliable cold storage is essential for maintaining product quality and meeting regulatory requirements. As Texas continues to grow as a hub for food production and distribution, advanced humidity management techniques become increasingly critical for maintaining competitive advantage and operational efficiency in temperature-sensitive industries.

This story is based on an article that was registered on the blockchain. The original source content used for this article is located at Newsworthy.ai
Article Control ID: 251685
